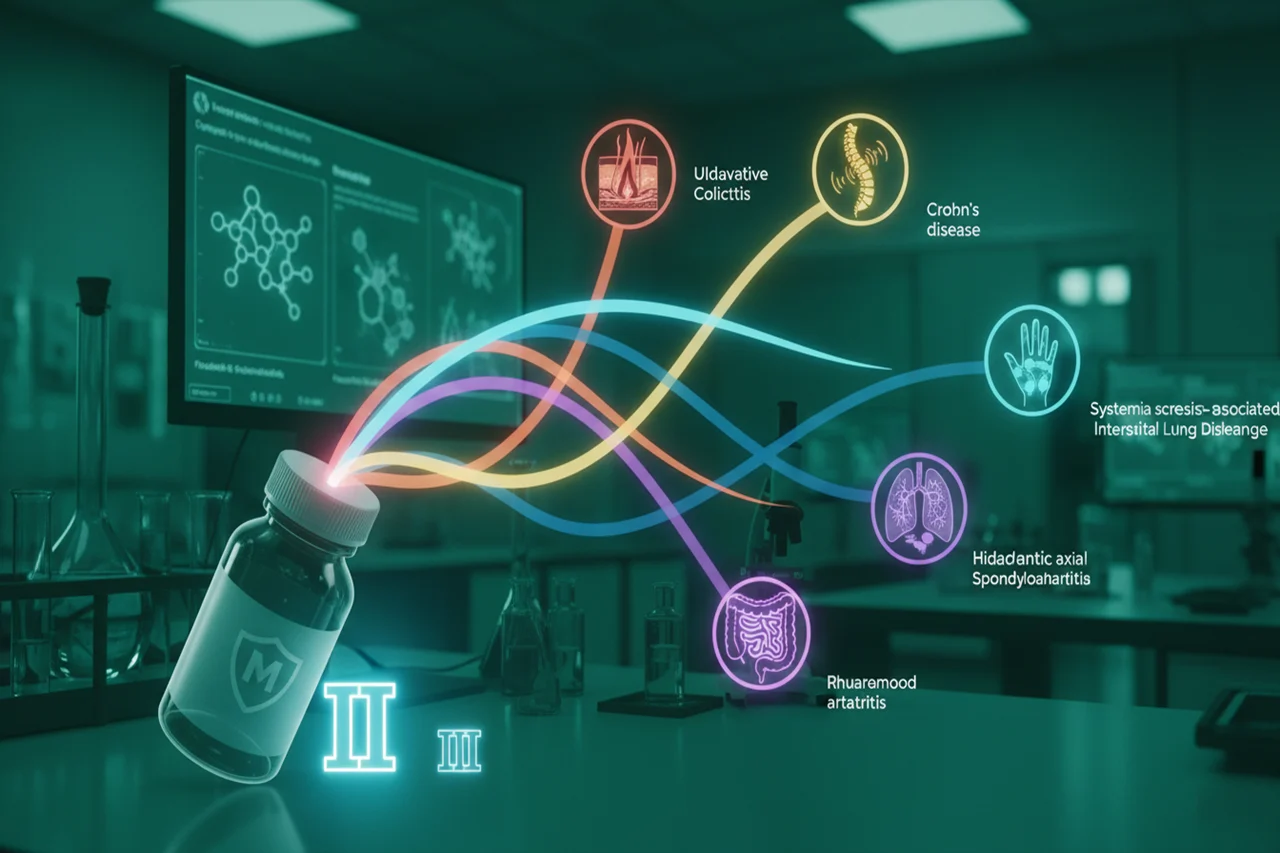
Rahway, N.J. – Merck, known as MSD outside the United States and Canada, announced the initiation of three new Phase 2b clinical trials to evaluate the safety and efficacy of tulisokibart (MK-7240), an investigational humanized monoclonal antibody designed to target tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-like cytokine 1A (TL1A). The new studies will assess tulisokibart in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (r-axSpA)—also known as ankylosing spondylitis—and rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
The three trials, all currently recruiting globally, include:
- MK-7240-012 (NCT06956235): A study evaluating tulisokibart in adults with moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa, a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by painful nodules and abscesses.
- MK-7240-013 (NCT07133633): A trial assessing tulisokibart in patients with radiographic axial spondyloarthritis, a progressive inflammatory disease affecting the spine and sacroiliac joints.
- MK-7240-014 (NCT07176390): A study investigating tulisokibart’s effects in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis, a systemic autoimmune disorder that primarily targets joints.
Together, these studies aim to enroll more than 640 participants worldwide, reflecting Merck’s growing commitment to advancing innovative therapies for patients with chronic immune-mediated conditions.
Advancing a Broad Immunology Pipeline
“Expanding our tulisokibart clinical development program underscores Merck’s dedication to addressing the burden of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases that affect millions worldwide,” said Dr. Aileen Pangan, Vice President and Head of Immunology, Global Clinical Development, Merck Research Laboratories. “We’re eager to further explore tulisokibart’s therapeutic potential across multiple conditions in both rheumatology and dermatology, as we work toward meaningful treatment advances for patients.”
The expansion brings the total number of diseases under tulisokibart investigation to six, positioning the antibody as a key candidate in Merck’s immunology pipeline.
A Next-Generation Approach to Inflammatory Disease
Tulisokibart (MK-7240) is a monoclonal antibody that targets TL1A (TNF-like cytokine 1A), a member of the TNF superfamily involved in regulating inflammation and fibrosis. TL1A is a promising therapeutic target because it plays a central role in multiple inflammatory pathways linked to autoimmune diseases. By selectively modulating TL1A signaling, tulisokibart may help restore immune balance and reduce inflammation across several disease settings.
The TL1A pathway has gained significant attention in recent years for its potential to improve treatment outcomes where current therapies, such as TNF inhibitors and IL-17 blockers, have shown limited effectiveness or tolerability. Merck’s tulisokibart program builds on this scientific momentum, exploring whether precise inhibition of TL1A can offer more targeted and durable disease control.
Broad Clinical Development Program Across Six Diseases
In addition to the three new Phase 2b trials, tulisokibart is also being evaluated in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD)—conditions with high unmet medical needs.
Merck’s ongoing studies include:
- ATLAS-UC (NCT06052059): A Phase 3 trial evaluating tulisokibart’s efficacy and safety in patients with ulcerative colitis (UC).
- ARES-CD (NCT06430801): A Phase 3 study focused on Crohn’s disease (CD).
- NCT05270668: A Phase 2 trial investigating tulisokibart in systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD).
By advancing clinical research across such a broad range of immune-mediated diseases, Merck aims to demonstrate tulisokibart’s versatility as a potential foundational therapy for inflammatory and fibrotic disorders.
Commitment to Addressing Immune-Mediated Diseases
Merck has made immunology and inflammation one of its strategic therapeutic focus areas, leveraging decades of scientific expertise in immunopathology, molecular biology, and translational medicine. The company’s research efforts aim to uncover shared pathways driving chronic inflammation and tissue damage across multiple diseases—thereby enabling a precision medicine approach to immune modulation.
“By targeting TL1A, tulisokibart represents a new generation of biologic therapy that could change how we treat complex inflammatory diseases,” added Dr. Pangan. “With these Phase 2b trials, we are one step closer to understanding how this mechanism can deliver meaningful clinical benefit across multiple disease states.”
Looking Ahead
As tulisokibart moves further into mid- and late-stage development, Merck’s immunology program continues to expand in scope and ambition. The company is pursuing biomarker-driven research to identify which patients are most likely to benefit from TL1A inhibition, while exploring combination strategies with other immune-targeted agents.
If successful, tulisokibart could become one of the first therapies to demonstrate broad disease-modifying potential across multiple autoimmune and inflammatory conditions. Merck’s integrated approach—spanning dermatology, rheumatology, gastroenterology, and pulmonology—illustrates its vision for developing cross-disease solutions that improve long-term outcomes and quality of life for patients living with chronic inflammation.
With these latest Phase 2b trials now underway, Merck continues to build momentum in delivering on that vision—advancing tulisokibart as a promising candidate in its next wave of innovative immunology therapies aimed at transforming patient care.
For an overview of Merck’s clinical development program in immunology, please click here.
About hidradenitis suppurativa (HS)
Hidradenitis suppurativa is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects hair follicles and is characterized by small, painful abscesses under the skin in areas of the body such as the armpits, groin, buttocks and breasts. Hidradenitis suppurativa affects a variable proportion of the population, with prevalence estimates ranging from 0.1% to 0.8%.
About radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (r-axSpA)
Radiographic axSpA (also known as ankylosing spondylitis) is characterized by chronic inflammation and pain involving the spine and the joints that connect the bottom of the spine to the pelvis. As its name suggests, damage associated with r-axSpA is visible on X-rays. Worldwide, it is thought to affect 0.1% to 1% of all people.
About rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by the inflammation of joints, which can lead to pain, swelling and stiffness. Rheumatoid arthritis can also affect other parts of the body, including the skin, eyes, mouth, heart and lungs. Globally, it is estimated that 17.9 million people are affected by RA, which represents a 13.2% increase since 1990.
About tulisokibart
Tulisokibart is an investigational humanized monoclonal antibody directed to a novel target, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-like cytokine 1A (TL1A), that is associated with both intestinal inflammation and fibrosis. Tulisokibart is thought to bind both soluble and membrane-bound human TL1A. Clinical studies suggest that tulisokibart may inhibit inflammatory pathways involved in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and help reduce intestinal fibrosis, which may be important in altering disease progression in IBD. Merck is developing tulisokibart for the treatment of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases including ulcerative colitis (UC), Crohn’s disease (CD), systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD), hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (r-axSpA), and rheumatoid arthritis(RA).